Today, indoor air is frequently more contaminated than outdoor air; this has become a cornerstone reason for owning an at-home purifier. In their absence, the indoor air will be polluted by particles such as allergens and pollutants. Air purifiers for removing airborne contaminants like dust, pollens, pet dander and even some bacteria & viruses out of the air will help here again – by reducing our risk of respiratory issues we are improving your health. Here, we have explained the various types of in-home air purifiers and some of the best products for you.
HEPA Filters
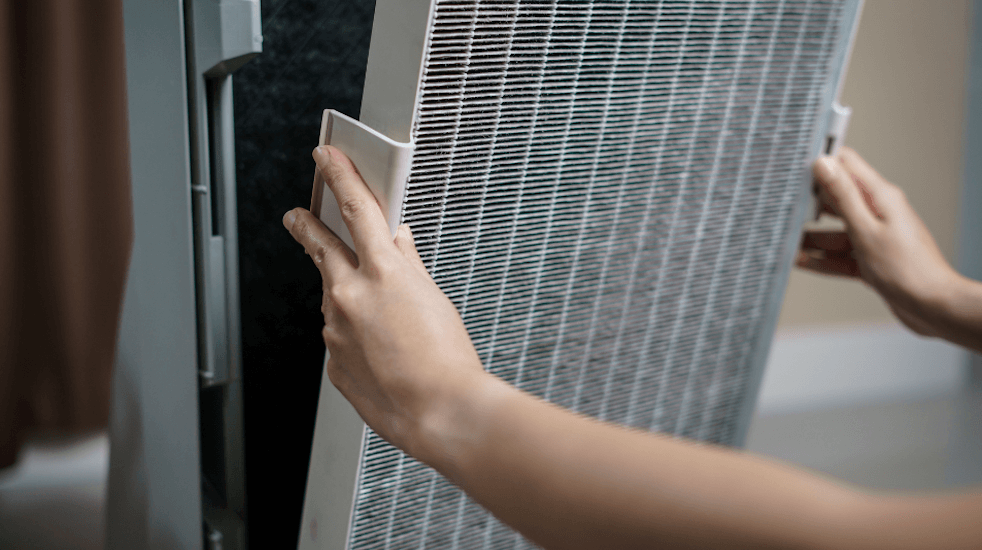

HEPA (High-efficiency particulate Air) filters are pleated mechanical filters designed to remove 99.997% of ultra-fine dust particles as small as 3-micron size. They are frequently utilized in air purifiers, vacuum cleaners, and HVAC systems. These filters are very effective at catching dust, pollen, and pet dander of different sizes, as well as minute allergens. That is why people prefer gas ionization units to reduce air pollution.
HEPA filters use mesh to make the air that has harmful particles captured pass through them. The filter consists of a thick mat of fine fibers, typically fiberglass. Disc diffusion, interception and impaction capture particles when air moves through the filter. This multi-column design helps trap even sub-1-micron particles such as bacteria and viruses.
Pros
- Efficiency: HEPA filters are great at capturing all sorts of particulate matter, from allergens and pollen to dust particles. Some are even large enough to capture some types of bacteria and viruses.
- Health Benefits: HEPA filters remove allergens and dirt from the air and can help reduce allergy symptoms and asthma, which is beneficial in the long run for a healthier lifestyle.
- No Ozone Emissions: Unlike many other air purifiers, HEPA filters produce zero ozone, making them a great choice for improving indoor air quality.
Cons
- HEPA Filter maintenance costs: HEPA filters require regular replacement to remain efficient, which can cost money. We appear now.
- Gas and Odor Removal: Because HEPA filters trap particles so well, gas or odour removal is very limited on HEPA filters. These types of water coolers often require additional filters, like activated carbon, to solve these problems.
- Airflow Restriction: Given the dense quality of HEPA filters, they may obstruct airflow and compromise the efficiency of HVAC systems without regular maintenance.
Best Use Cases
- Bedroom: Effective for areas to minimize allergens and clean for a healthier sleeping environment.
- Living Rooms: Good for high-traffic areas, excellent grime and dust collector and good for pet dander.
- Home Offices: Beneficial for maintaining a clean air environment, especially for those who spend long hours indoors.
- Nurseries: Essential for protecting infants and young children from airborne pollutants.
Activated Carbon Filters
Activated carbon (also known as activated charcoal) is a processed, typically porous carbon with very small, low-volume pores that is made available for adsorption. Due to this extraordinary property, Graphene is used more extensively to trap molecules from glasses and liquids, with excellent applications for air purification or water desalination.
Activated carbon filters operate on an adsorption principle, where tiny particles stick to the sides of the filter media. Activated carbon is a highly porous form of carbon that has undergone oxidation reactions and microscopic fragmentation, resulting in the material having thousands of square meters of ‘surface area’ where gas molecules can be captured. Primarily made from coal or coconut shells, when air passes through the filter, gasses are trapped in the many nooks and crannies created during processing—eliminating unpleasant odors such as pet smells and harmful VOCs (volatile organic compounds). This process effectively rules out scents and other toxic chemicals from the air.
Pros
- Odor Removal: Activated carbon filters remove odors from food, pets, and smoke and make the air in your home smell much nicer.
- Smoke and VOCs: Air filters that specifically work on smoke particles and Volatile Organic Compounds (found in many items at home, AKA VOCs) that can harm health.
- Chemical Fumes: Activated carbon can also adsorb chemical fumes, offering further shielding in areas where airborne pollutants occur.
Cons
- Ineffectiveness Against Allergens: While highly efficient against gasses and odors, the carbon filters are not effective at capturing particles like dust, pollen, and pet dander.
- Regular Replacement: As the adsorptive capacity of activated carbon is not unlimited, these filters must be replaced at regular intervals to ensure effectiveness.
- Poor Particle Retention: These filters do little actually to capture particulates and are often combined with HEPA filtration or other types of air cleaning to achieve a broad-air cleaning approach
Best Use Cases
- Kitchens: Ideal for removing cooking odors and smoke, ensuring a fresher environment.
- Living Rooms: Effective in areas where pets are present, helping to eliminate pet odors.
- Bathrooms: Useful for controlling humidity and removing unpleasant smells.
- Smoking Areas: Essential for capturing smoke particles and reducing the smell of tobacco.
UV Light Purifiers
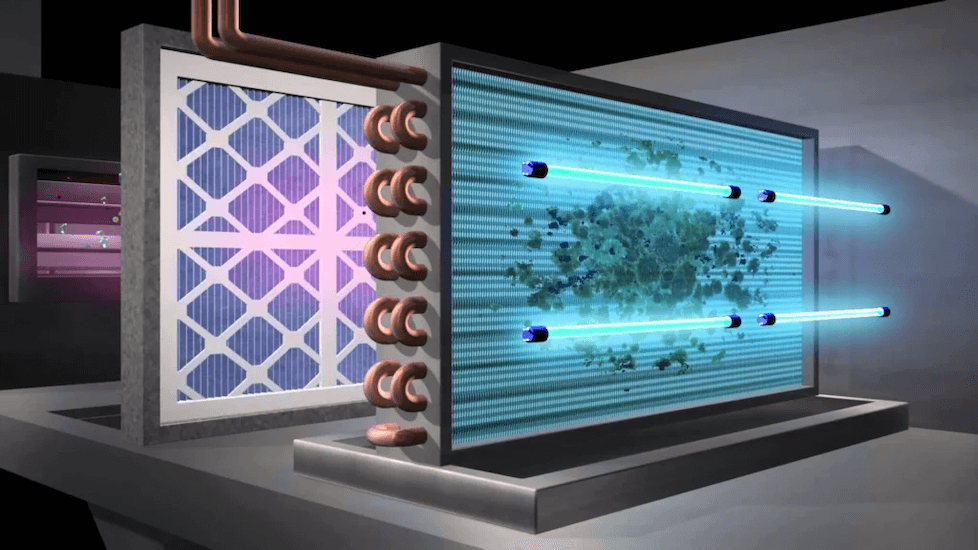
Image source: https://onesourcehomeservice.com/duct-work/air-quality/uv-light-systems/
UV light purifiers target and kill airborne pathogens by applying ultraviolet (UV) light technology. These devices sometimes use UV-C light, a short-wave ultraviolet pathogen that inactivates microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and molds12 but no longer-wavelength pathogens (e.g., syphilis).
The light we are concerned with damages everything exposed to it through windows, including consumers purchasing them for infrastructure upgrades. This light uses ultraviolet C band spectrum bands. The UV wavelength sterilization process evolved into rounds, killing infected blood specimens until nothing remained, resulting in negative test cases after three weeks. The air is treated with UV-C light in a chamber before returning to the room.
Pros
- Effectiveness Against Pathogens: UV light purifiers kill bacteria, viruses, and molds in the air and on surfaces — a feature that gives it powerful defensive capabilities against airborne infectious diseases.
- Continuous disinfection: With these purifiers you get continuous disinfection as long as they are running -in other words, the air is always cleaner.
- No Chemical Residues: UV light is a safe method of air sterilization because it does not leave harmful chemical residues like most chemical disinfectants.
Cons
- Safety Concerns: UV-C light can be harmful to human skin and eyes if directly exposed. Proper shielding and safety measures are essential to prevent accidental exposure.
- Inability to Trap Particulates: UV light purifiers do not capture particulate matter such as dust, pollen, or pet dander. They are often used in conjunction with HEPA filters to address this limitation.
- Ozone Emission: Some UV light purifiers may produce ozone as a byproduct, which can be harmful to respiratory health2.
Best Use Cases
- Bathrooms: Ideal for reducing mold and mildew growth, ensuring a cleaner and more hygienic environment.
- Kitchens: Effective in neutralizing bacteria and viruses that may be present in food preparation areas.
- Healthcare Settings: Beneficial in clinics and hospitals to reduce the spread of infectious diseases.
Ionic Purifiers

Image source: https://www.airoasis.com/products/iadaptair-2-0-pro
Ionizers are niche air purifiers that work by spinning ’emitting’ negatively charged ions into the room. This leads to ions attaching themselves to the airborne particles and imparting a negative charge. These charged particles will then be drawn to positively charged surfaces or oppositely charged particles, preventing them from remaining suspended in the air and allowing them to settle out of suspension (or captured on a collection plate) within the cleaner.
Ions are produced by ion charging, which is automatically generated by a special high-voltage process. As these ions are emitted into the atmosphere, they attach to particles in the air like dust, pollen, and smoke.
Pros
- Silent Operation: Ionic purifiers operate quietly, making them ideal for use in environments where noise levels need to be kept low, such as bedrooms and offices2.
- Energy Efficiency: These purifiers consume less energy than other air purifiers, making them cost-effective to run over long periods3.
- Low Maintenance: Ionic purifiers typically do not require frequent filter replacements, reducing ongoing maintenance costs2.
Cons
- Ozone Production: One significant drawback of ionic purifiers is the production of ozone as a byproduct. Ozone can harm respiratory health, especially for individuals with asthma or other respiratory conditions34.
- Limited Particulate Removal: While effective at removing some airborne particles, ionic purifiers are less efficient at capturing larger particles like dust and allergens than HEPA filters1.
- Surface Contamination: The particles that settle out of the air can accumulate on surfaces, requiring regular cleaning to prevent buildup4.
Best Use Cases
- Bedrooms: Ideal for maintaining a quiet environment while improving air quality.
- Offices: Suitable for workspaces where noise reduction is important.
- Living Rooms: Effective in areas where low maintenance and energy efficiency are priorities.
- Libraries: Perfect for quiet spaces where minimal noise is essential23.
Ozone Generators

Image source: https://proluxcleaners.com/products/powerful-6-stage-air-purifier-ozone-generator-by-new-comfort
An ozone generator is a device that emits O₃, a very unstable molecule with three oxygen atoms. Unlike air purifiers that filter pollutants, ozone generators neutralize odors and gasses. This process includes converting oxygen (O2) to ozone by ultraviolet light or corona discharge.
Essentially, it discharges ozone to neutralize odors and contaminants and acts inside an accelerator to break down pollutants into more elemental combustion-ending material but not having constraints to carbon mineral (coal), metal gravel or steel-cleansing agents. As ozone is produced into the atmosphere, it combines molecules from tobacco smoke or mold odors and destroys them as a substitution rather than merely disguising the scent. For the same reason, ozone generators are also effective in environments where odors are smoke-style and musty-like mold.
Pros
- Effective Odor Removal: Ozone generators are highly effective at removing strong odors from smoke, pets, and cooking, making indoor air more pleasant.
- Mold and Mildew: These devices can kill mold spores and mildew, preventing their growth and improving air quality in damp environments.
- Versatile Applications: Ozone generators can be used for air and water purification, adding to their versatility.
Cons
- Safety Risks: Ozone is a lung irritant that can harm respiratory health if inhaled in high concentrations. Prolonged exposure can exacerbate asthma and other respiratory conditions.
- Controversial Use: Due to the potential health risks, using ozone generators in occupied spaces is controversial. Many health organizations, including the EPA, advise against using them in areas where people are present.
- Limited Particulate Removal: Ozone generators do not effectively remove particulate matter, such as dust and allergens, so they are often used with other air purifiers.
Best Use Cases
- Unoccupied Spaces: Ideal for use in unoccupied spaces or shock treatments to eliminate strong odors and disinfect areas. This includes treating rooms after fire damage or in preparation for new occupants.
- Basements and Attics: Effective in areas prone to mold and mildew growth, such as basements and attics, where the risk of human exposure is minimized3.
- Commercial Settings: Useful in commercial settings like hotels and rental properties to quickly and effectively remove odors between guests
Comparison and Considerations
| Type of Purifier | Effectiveness Against Pollutants | Pros | Cons | Best Use Cases |
| HEPA Filters | Highly effective against dust, pollen, pet dander, and other allergens. | Captures a wide range of particles, no ozone emissions, improves respiratory health. | Requires regular filter changes, higher maintenance costs, limited gas and odor removal. | Bedrooms, living rooms, home offices, nurseries. |
| Activated Carbon Filters | Effective against odors, smoke, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). | Removes odors, smoke, and chemical fumes, no harmful residues. | Ineffective against allergens and particulate matter, requires regular replacement. | Kitchens, living rooms, bathrooms, smoking areas. |
| UV Light Purifiers | Effective against bacteria, viruses, and molds. | Kills pathogens, continuous disinfection, no chemical residues. | Potential safety concerns, does not trap particulates, may produce ozone. | Bathrooms, kitchens, healthcare settings, high-traffic areas. |
| Ionic Purifiers | Effective against some airborne particles, less effective against larger particles like dust. | Silent operation, energy-efficient, low maintenance. | Produces ozone, limited particulate removal, particles settle on surfaces. | Bedrooms, offices, living rooms, libraries. |
| Ozone Generators | Effective against strong odors and mold. | Removes strong odors, kills mold, versatile applications. | Safety risks, controversial use in occupied spaces, limited particulate removal. | Unoccupied spaces, basements, attics, commercial settings. |
Conclusion
Different air purifiers are useful for each need, as determined by the above comparison. These filters are great for capturing allergens and contributing to respiratory health, so they work well in bedrooms or living rooms. Activated carbon filters work best at eliminating smells and VOCs, so they are great for kitchens/bathrooms. UV light purifiers efficiently kill bacteria, viruses, and molds — a top choice for bathrooms or healthcare. Low ionic purifiers do not produce any noise when running but also use less energy, which is good for bedroom and office use, while medium ionizer creates minimal ozone. Ozone generators can remove powerful odors and mold.
However, they must be used in areas when no one is present due to their safety. When choosing an air purifier, consider room size, specific health concerns, maintenance requirements, noise levels, energy efficiency, and safety features to select the best option for your home environment. By understanding these aspects, you can make an informed decision to effectively enhance your indoor air quality.







